Cyclical unemployment refers to the Unemployment caused by regular fluctuations in the economy correlated with the short-run ups and downs of economic activity, that occur within the business cycle.
When an economy is doing great, cyclical unemployment usually goes down, because the total economic output(GDP) is high and the demand for labour is higher as well.
What Causes Cyclical Unemployment
One primary determinant of the demand for labour from firms shows they perceive the state of the macroeconomy.
If, firms believe that business is expanding, then at any given wage they will desire to hire a greater quantity of labour and the labour demand curve shifts to the right.
Conversely, if firms perceive that the economy is slowing down or entering a recession businesses will wish to hire a lower quantity of labour at any given wage, and the labour demand curve will shift to the left.
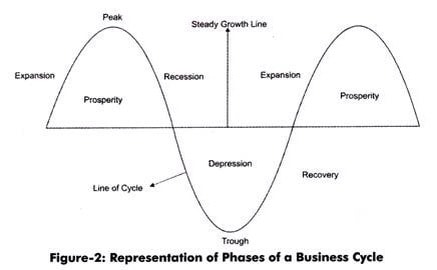
The shift in unemployment caused by the economy shifting from growth to a recession in the business cycle is known as cyclical unemployment.
When economic output or the business cycle is low the cyclical unemployment will increase.
Cyclical unemployment is the effect of businesses having less demand for workers to employ all those who are looking for jobs at within the business cycle.
Most business cycles are repetitive, with the downturn eventually turning to an upturn again, followed by another recession, recovery and so on.
Effects
Cyclical unemployment can set a unstoppable domino effect.
Because the recently jobless people will have less to no disposable income, this lay-off further reduces demand and business income, leading to even more layoffs.
If not interfere, this domino effect will continue until supply has lowered to meet the reduced demand.
We have seen this domino effect during the 2008 recession, is, which lasted
What indeed ended the 2008 recession is only the infusion of hundreds of billions of dollars into the US and European banking system, stopped an entire crash of the world’s financial markets.
Examples
Construction workers and architectures may be laid off during a recession when people are buying fewer houses because they simply can’t afford them there is no point for builders to construct new houses.
When people buy fewer houses, There will be less demand for construction workers.
Cyclical Unemployment Rate
The cyclical unemployment rate is the deviation between the natural unemployment rate and the current rate.
The natural unemployment rate combines frictional, structural, classical, and seasonal unemployment.
You can Subtract those from the unemployment rate to calculate the cyclical unemployment rate.
